Dr. KC Bierlich, Postdoctoral Scholar, OSU Department of Fisheries, Wildlife, & Conservation Sciences, Geospatial Ecology of Marine Megafauna (GEMM) Lab
In a previous blog, I discussed the importance of incorporating measurement uncertainty in drone-based photogrammetry, as drones with different sensors, focal length lenses, and altimeters will have varying levels of measurement accuracy. In my last blog, I discussed how to incorporate photogrammetric uncertainty when combining multiple measurements to estimate body condition of baleen whales. In this blog, I will highlight our recent publication in Frontiers in Marine Science (https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.867258) led by GEMM Lab’s Dr. Leigh Torres, Clara Bird, and myself that used these methods in a collaborative study using imagery from four different drones to compare gray whale body condition on their breeding and feeding grounds (Torres et al., 2022).
Most Eastern North Pacific (ENP) gray whales migrate to their summer foraging grounds in Alaska and the Arctic, where they target benthic amphipods as prey. A subgroup of gray whales (~230 individuals) called the Pacific Coast Feeding Group (PCFG), instead truncates their migration and forages along the coastal habitats between Northern California and British Columbia, Canada (Fig. 1). Evidence from a recent study lead by GEMM Lab’s Lisa Hildebrand (see this blog) found that the caloric content of prey in the PCFG range is of equal or higher value than the main amphipod prey in the Arctic/sub-Arctic regions (Hildebrand et al., 2021). This implies that greater prey density and/or lower energetic costs of foraging in the Arctic/sub-Arctic may explain the greater number of whales foraging in that region compared to the PCFG range. Both groups of gray whales spend the winter months on their breeding and calving grounds in Baja California, Mexico.
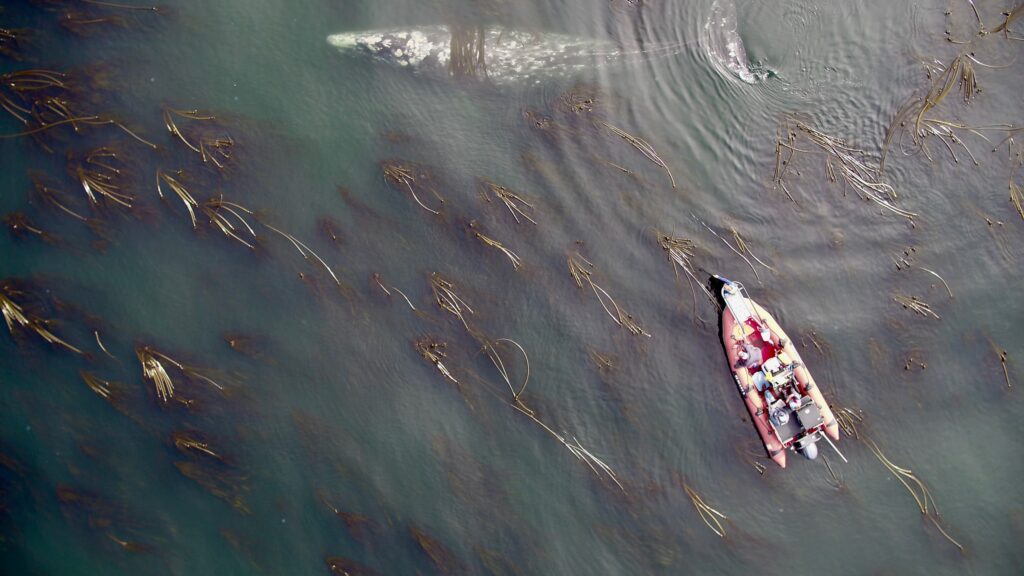

In January 2019 an Unusual Mortality Event (UME) was declared for gray whales due to the elevated numbers of stranded gray whales between Mexico and the Arctic regions of Alaska. Most of the stranded whales were emaciated, indicating that reduced nutrition and starvation may have been the causal factor of death. It is estimated that the population dropped from ~27,000 individuals in 2016 to ~21,000 in 2020 (Stewart & Weller, 2021).
During this UME period, between 2017-2019, the GEMM Lab was using drones to monitor the body condition of PCFG gray whales on their Oregon coastal feeding grounds (Fig. 1), while Christiansen and colleagues (2020) was using drones to monitor gray whales on their breeding grounds in San Ignacio Lagoon (SIL) in Baja California, Mexico. We teamed up with Christiansen and colleagues to compare the body condition of gray whales in these two different areas leading up to the UME. Comparing the body condition between these two populations could help inform which population was most effected by the UME.
The combined datasets consisted of four different drones used, thus different levels of photogrammetric uncertainty to consider. The GEMM Lab collected data using a DJI Phantom 3 Pro, DJI Phantom 4, and DJI Phantom 4 Pro, while Christiansen et al., (2020) used a DJI Inspire 1 Pro. By using the methodological approach described in my previous blog (here, also see Bierlich et al., 2021a for more details), we quantified photogrammetric uncertainty specific to each drone, allowing cross-comparison between these datasets. We also used Body Area Index (BAI), which is a standardized relative measure of body condition developed by the GEMM Lab (Burnett et al., 2018) that has low uncertainty with high precision, making it easier to detect smaller changes between individuals (see blog here, Bierlich et al., 2021b).
While both PCFG and ENP gray whales visit San Ignacio Lagoon in the winter, we assume that the photogrammetry data collected in the lagoon is mostly of ENP whales based on their considerably higher population abundance. We also assume that gray whales incur low energetic cost during migration, as gray whale oxygen consumption rates and derived metabolic rates are much lower during migration than on foraging grounds (Sumich, 1983).
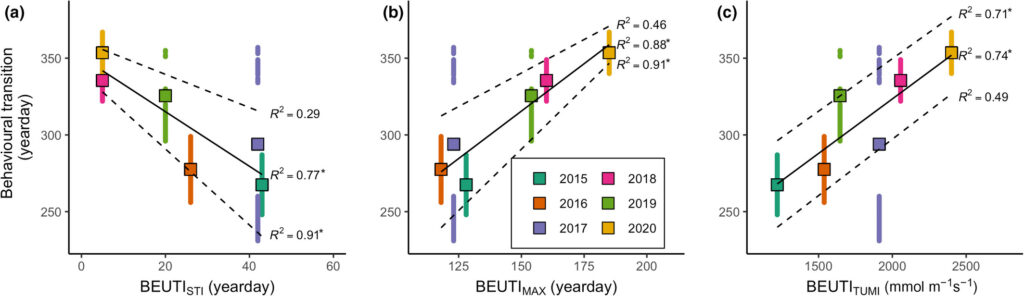
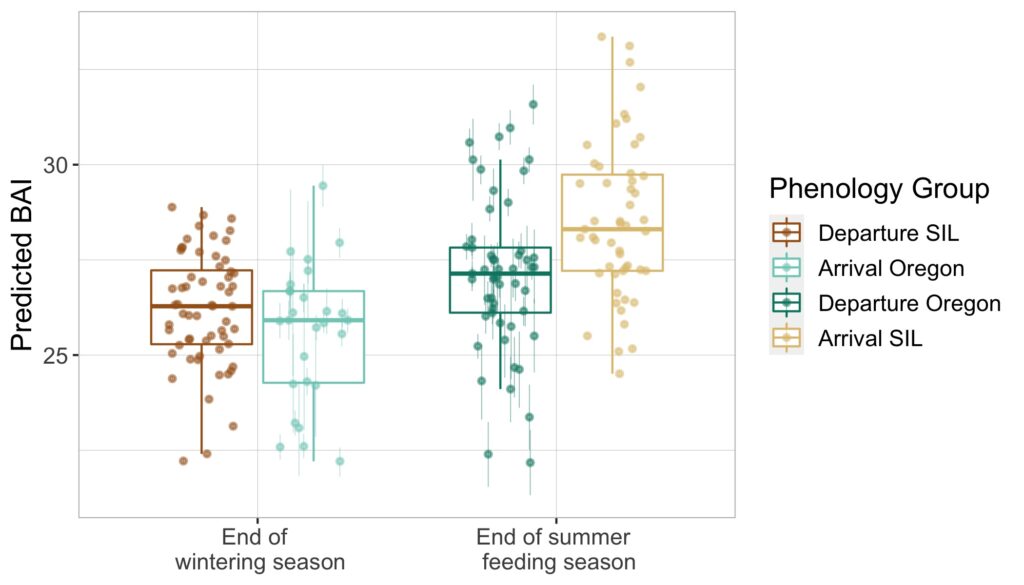
Interestingly, we found that gray whale body condition on their wintering grounds in San Ignacio Lagoon deteriorated across the study years leading up to the UME (2017-2019), while the body condition of PCFG whales on their foraging grounds in Oregon concurrently increased. These contrasting trajectories in body condition between ENP and PCFG whales implies that dynamic oceanographic processes may be contributing to temporal variability of prey available in the Arctic/sub-Arctic and PCFG range. In other words, environmental conditions that control prey availability for gray whales are different in the two areas. For the ENP population, this declining nutritive gain may be associated with environmental changes in the Arctic/sub-Arctic region that impacted the predictability and availability of prey. For the PCFG population, the increase in body condition across years may reflect recovery of the NE Pacific Ocean from the marine heatwave event in 2014-2016 (referred to as “The Blob”) that resulted with a period of low prey availability. These findings also indicate that the ENP population was primarily impacted in the die-off from the UME.
Surprisingly, the body condition of PCFG gray whales in Oregon was regularly and significantly lower than whales in San Ignacio Lagoon (Fig. 2). To further investigate this potential intrinsic difference in body condition between PCFG and ENP whales, we compared opportunistic photographs of gray whales feeding in the Northeastern Chukchi Sea (NCS) in the Arctic collected from airplane surveys. We found that the body condition of PCFG gray whales was significantly lower than whales in the NCS, further supporting our finding that PCFG whales overall have lower body condition than ENP whales that feed in the Arctic (Fig. 3).

This difference in body condition between PCFG and ENP gray whales raises some really interesting and prudent questions. Does the lower body condition of PCFG whales make them less resilient to changes in prey availability compared to ENP whales, and thus more vulnerable to climate change? If so, could this influence the reproductive capacity of PCFG whales? Or, are whales that recruit into the PCFG adapted to a smaller morphology, perhaps due to their specialized foraging tactics, which may be genetically inherited and enables them to survive with reduced energy stores?
These questions are on our minds here at the GEMM Lab as we prepare for our seventh consecutive field season using drones to collect data on PCFG gray whale body condition. As discussed in a previous blog by Dr. Alejandro Fernandez Ajo, we are combining our sightings history of individual whales, fecal hormone analyses, and photogrammetry-based body condition to better understand gray whales’ reproductive biology and help determine what the consequences are for these PCFG whales with lower body condition.
Did you enjoy this blog? Want to learn more about marine life, research, and conservation? Subscribe to our blog and get a weekly message when we post a new blog. Just add your name and email into the subscribe box below.
References
Bierlich, K. C., Hewitt, J., Bird, C. N., Schick, R. S., Friedlaender, A., Torres, L. G., … & Johnston, D. W. (2021). Comparing Uncertainty Associated With 1-, 2-, and 3D Aerial Photogrammetry-Based Body Condition Measurements of Baleen Whales. Frontiers in Marine Science, 1729.
Bierlich, K. C., Schick, R. S., Hewitt, J., Dale, J., Goldbogen, J. A., Friedlaender, A.S., et al. (2021b). Bayesian Approach for Predicting Photogrammetric Uncertainty in Morphometric Measurements Derived From Drones. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 673, 193–210. doi: 10.3354/meps13814
Burnett, J. D., Lemos, L., Barlow, D., Wing, M. G., Chandler, T., & Torres, L. G. (2018). Estimating morphometric attributes of baleen whales with photogrammetry from small UASs: A case study with blue and gray whales. Marine Mammal Science, 35(1), 108–139.
Christiansen, F., Rodrı́guez-González, F., Martı́nez-Aguilar, S., Urbán, J., Swartz, S., Warick, H., et al. (2021). Poor Body Condition Associated With an Unusual Mortality Event in Gray Whales. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 658, 237–252. doi:10.3354/meps13585
Hildebrand, L., Bernard, K. S., and Torres, L. G. (2021). Do Gray Whales Count Calories? Comparing Energetic Values of Gray Whale Prey Across Two Different Feeding Grounds in the Eastern North Pacific. Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.683634
Stewart, J. D., and Weller, D. (2021). Abundance of Eastern North Pacific Gray Whales 2019/2020 (San Diego, CA: NOAA/NMFS)
Sumich, J. L. (1983). Swimming Velocities, Breathing Patterns, and Estimated Costs of Locomotion in Migrating Gray Whales, Eschrichtius Robustus. Can. J. Zoology. 61, 647–652. doi: 10.1139/z83-086
Torres, L.G., Bird, C., Rodrigues-Gonzáles, F., Christiansen F., Bejder, L., Lemos, L., Urbán Ramírez, J., Swartz, S., Willoughby, A., Hewitt., J., Bierlich, K.C. (2022). Range-wide comparison of gray whale body condition reveals contrasting sub-population health characteristics and vulnerability to environmental change. Frontiers in Marine Science. 9:867258. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.867258