By Nina Mahalingam, University of California Davis, OSU CEOAS REU program
Hello! I’m Nina Mahalingam, a rising junior at the University of California, Davis studying biochemistry and molecular biology. Growing up in New Hampshire and Massachusetts, the Boston Aquarium was practically in my backyard – and with just one feel of a touch tank, a lifelong affinity for marine sciences began. CEOAS has provided me with a grand opportunity to pursue this passion, and I can’t wait to dip my toes into the salt water!

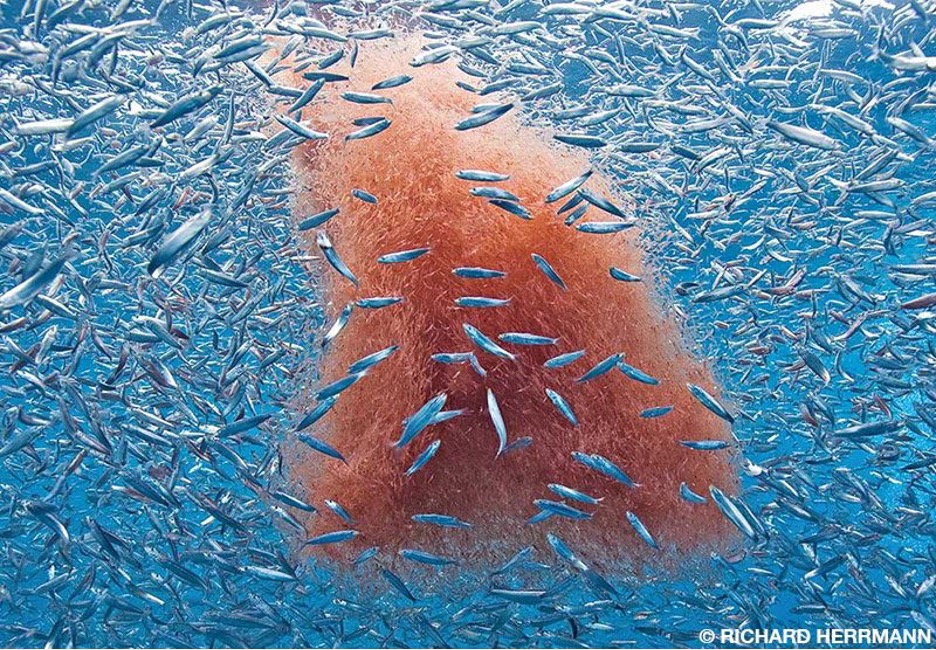
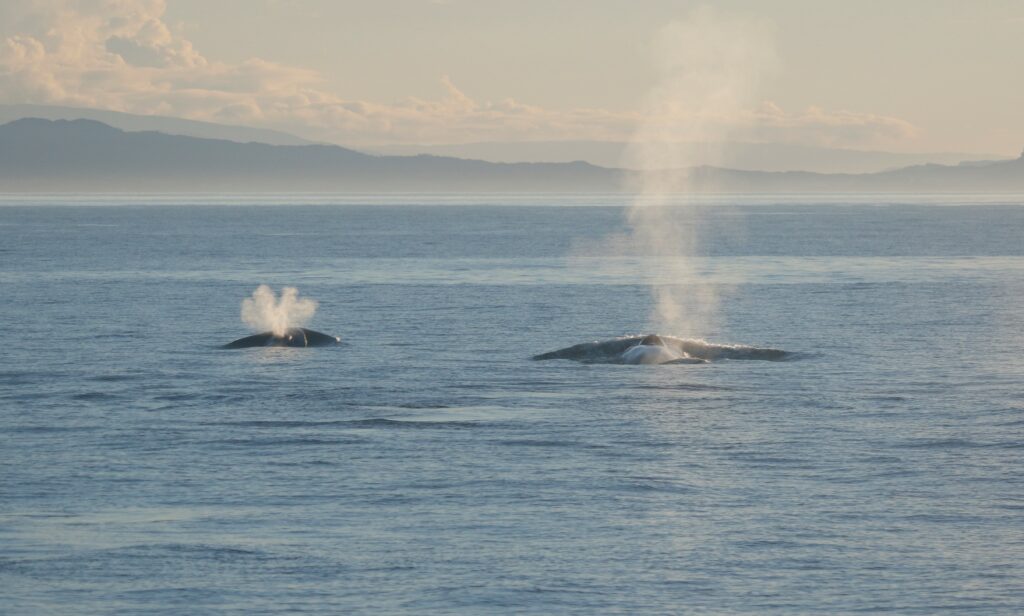
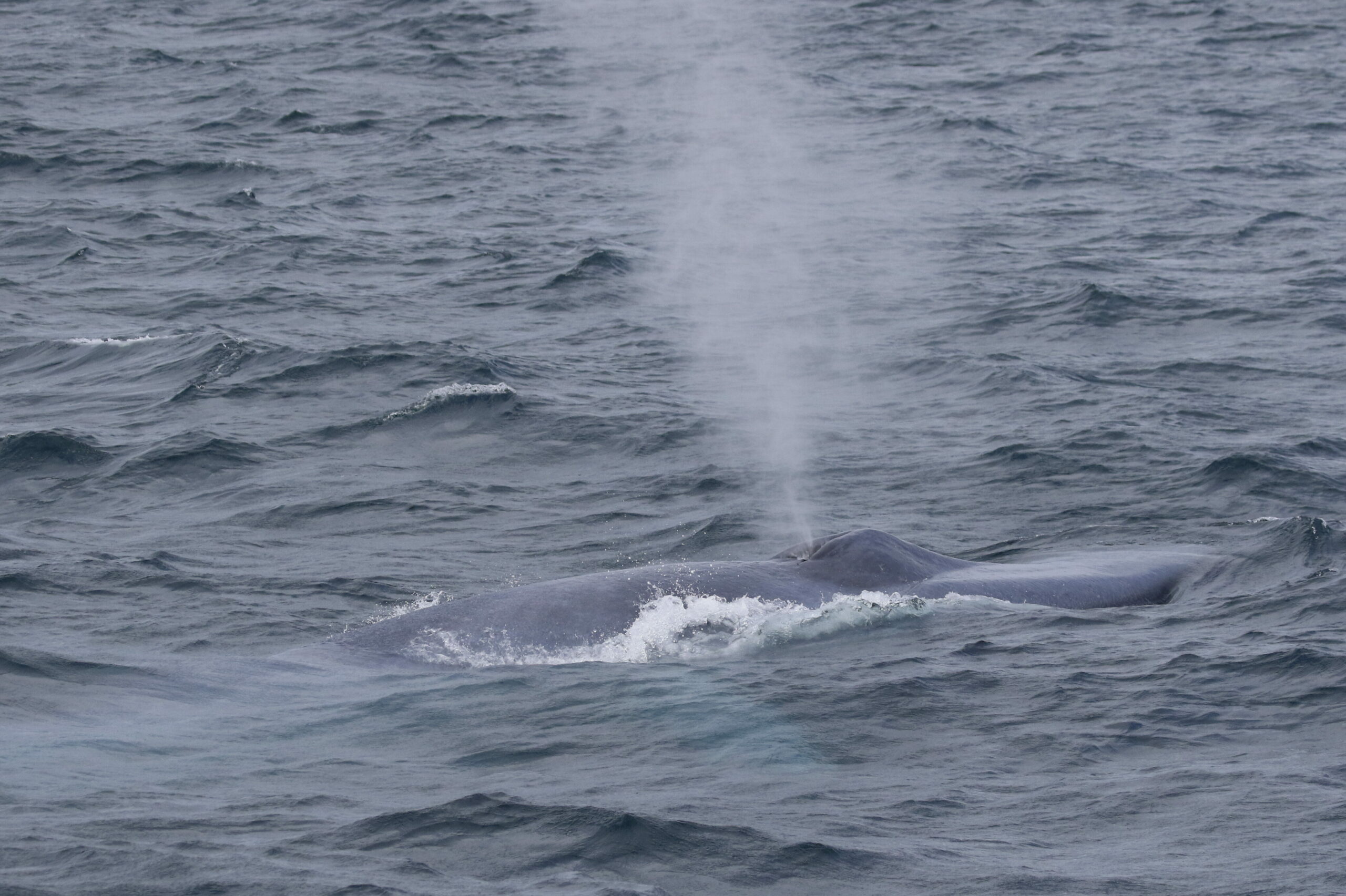
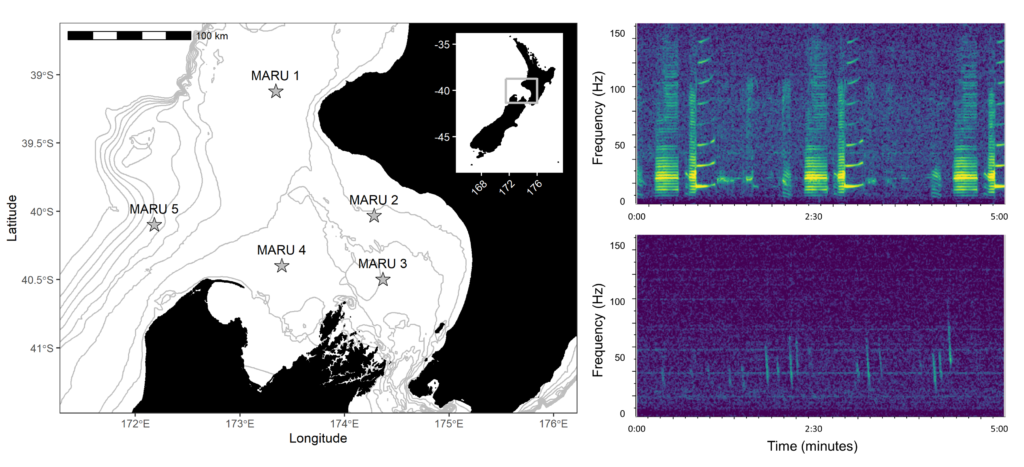
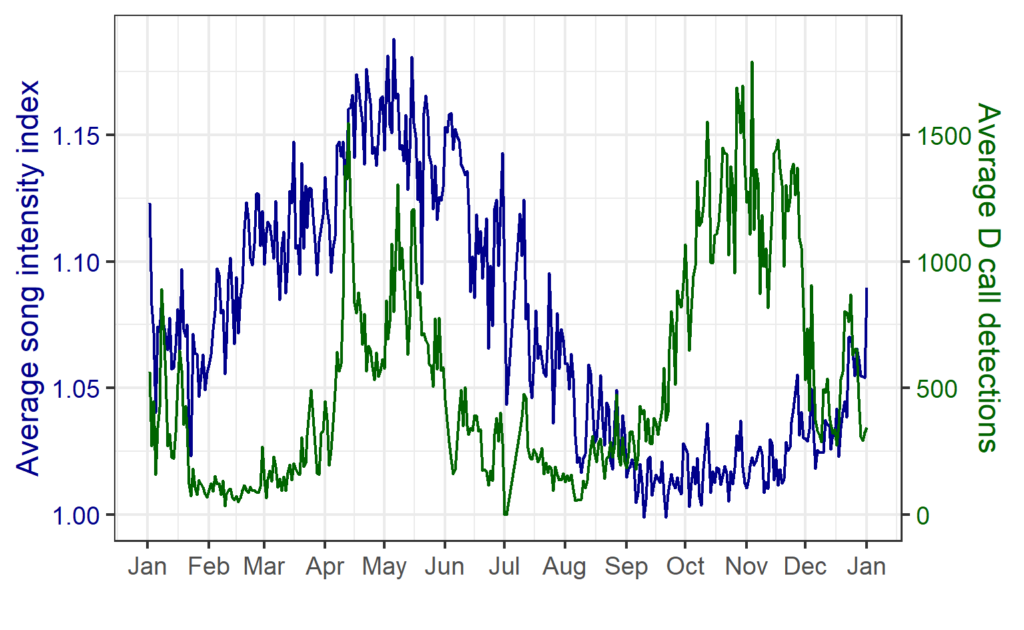
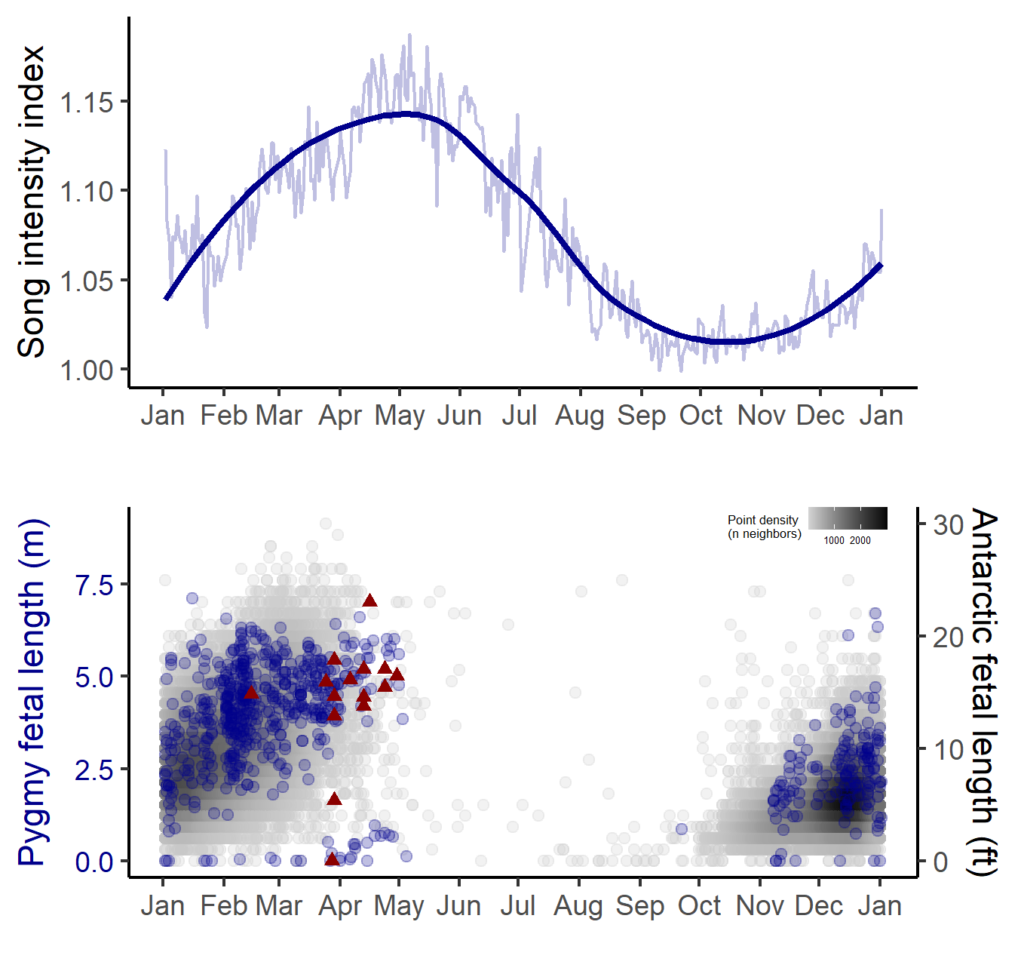
Here at OSU, I’m researching how our tiny friends, the krill, can provide a krill-uminating perspective on trophic ecology and the vitality of marine ecosystems by investigating the caloric content of an understudied species of krill off the coast of New Zealand. Nyctiphanes australis serves as a key prey species to numerous higher trophic levels. Limited knowledge exists regarding the distribution of N. australis in the South Taranaki Bight (STB), with only a handful of studies focused exclusively on the species. The majority of recent information available on the species in the STB came out of research on blue whales and their foraging behaviors (e.g., Barlow et al., 2020). However, given that the spatial distribution of N. australis directly influences the distribution of predator species that depend on them for sustenance (Barlow et. al. 2020), studying the krill may yield a more comprehensive understanding of blue whale behavior as well as ecosystem resilience.

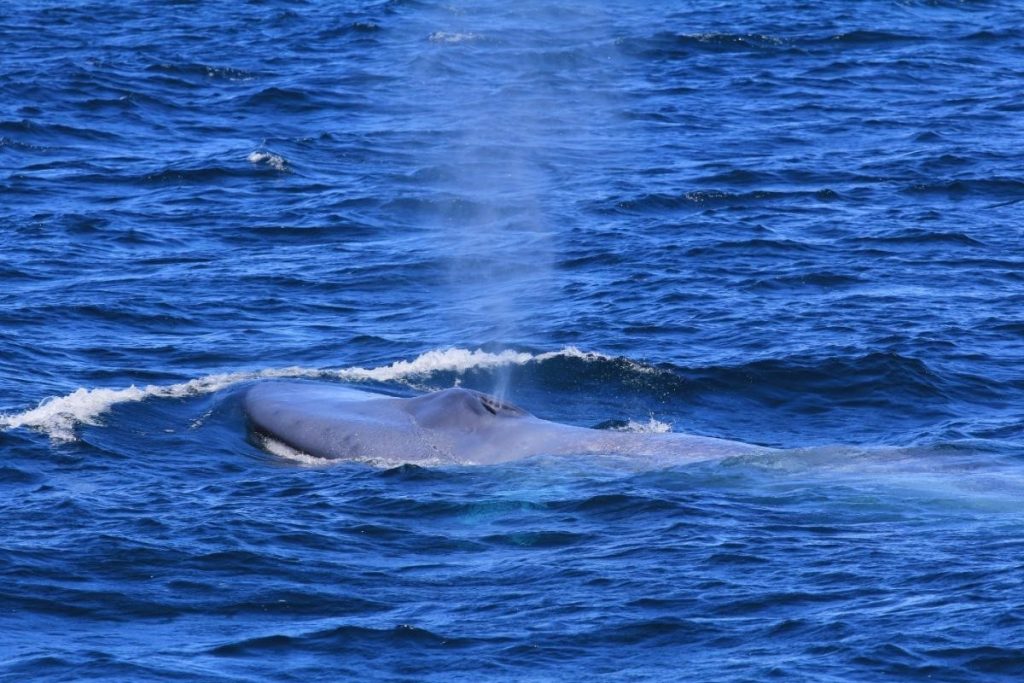
Seawater temperatures around New Zealand have been increasing since 1981 (Sutton & Bowen, 2019), and there is a growing concern about the implications to marine life. In particular, increasing ocean temperatures have had significant impacts on local aquaculture and fisheries (Sutton et al. 2005; Bowen et al. 2017). Although warming trends along the North Island, north of East Cape, have been more severe (around 0.4℃ increase per decade), warming has also been observed in the central and western areas of the STB, averaging around 0.15-0.20℃ increase per decade (Sutton & Bowen, 2019). During Marine Heat Waves (MHWs) (data collected between 2002 and 2018), warming anomalies were observed to decrease phytoplankton presence (Chiswell & Sutton, 2020). Being krill’s primary food source, this suggests a consequent decrease in krill health and reproduction. A recent study on blue whale reproductive patterns in the STB found that whale feeding activity decreased during MHWs, leading to a decline in their reproductive activity during the following breeding season (Barlow et al., 2020). Concurrently, the study observed that there were less krill aggregations and that they were less dense on average (Barlow et al., 2020). This is presumed to be a result of less upwelling nutrients, and therefore poor conditions for krill feeding and reproduction. These findings indicate that the absence of their primary food source, krill, during MHWs can lead to severely negative consequences for the blue whale populations (Barlow et al., 2023).
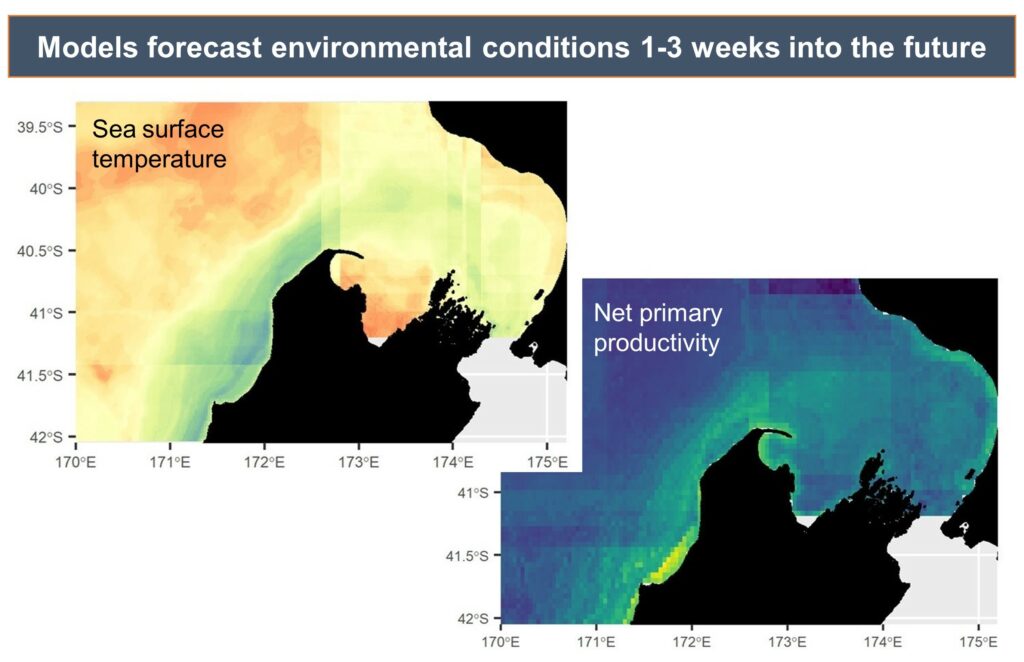
Anthropogenic activity in the STB, including high vessel traffic, as well as petroleum and mineral exploration and extraction activities, has also been identified as a threat to the local blue whale population (Torres et. al., 2013). Given the cultural significance of the blue whales in this region, there is an urgent need for improved, dynamic management practices in the STB that can be achieved using predictive models to forecast blue whale spatial distribution. Using environmental factors to inform predictive spatial distribution models (SDMs) of blue whales (Redfern et al. 2006, Elith & Leathwick 2009), Barlow et al. (2021) designed a blue whale forecasting tool for managers and decision-makers in New Zealand.
Given the ecological and cultural significance of blue whales and their krill prey in the STB, a Project SAPPHIRE (Synthesis of Acoustics, Physiology, Prey, and Habitat in a Rapidly changing Environment) was developed to examine the impacts of climate change on the health of these crucial species. The overarching goal of Project SAPPHIRE is to measure prey (krill) and predator (blue whales) response to environmental change off the coast of New Zealand. Despite forecasts of high probability of occurrence of blue whales in the STB during the first field season conducted in January-February 2024, both the blue whales and their krill prey were scarce, and it is currently unclear why. My research will focus on examining the calorie content of N. australis in order to advance understanding of how they fulfill the energetic needs of blue whales. Thus, this data can inform future SDMs to forecast impacts of climate change on New Zealand’s marine ecosystem.

This project has already proven tricky – but I’m ready to embrace the challenge. I would like to thank the CEOAS REU program as well as my mentors Kim Bernard, Rachel Kaplan, and Abby Tomita for their continued support. I can’t wait to see what this summer brings!
References
Barlow DR, Klinck H, Ponirakis D, Branch TA, Torres LG. 2023. Environmental conditions and marine heatwaves influence blue whale foraging and reproductive effort. Ecol Evol. 2023;13:e9770.
Barlow D, Kim S. Bernard, Pablo Escobar-Flores, Daniel M. Palacios, Leigh G. 2020. Torres Links in the trophic chain: modeling functional relationships between in situ oceanography, krill, and blue whale distribution under different oceanographic regimes. Marine Ecology Progress Series.
Sutton, P.J.H., & Bowen, M. 2019. Ocean temperature change around New Zealand over the last 36 years. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 53(3), 305–326.
Sutton P.J.H., Bowen M, Roemmich D. 2005. Decadal temperature changes in the Tasman Sea. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research. 39:1321–1329.
Bowen M, Markham J, Sutton P, Zhang X, Wu Q, Shears N, Fernandez D. 2017. Interannual variability of sea surface temperatures in the Southwest Pacific and the role of ocean dynamics. Journal of Climate.
Stephen M. Chiswell & Philip J. H. Sutton. 2020. Relationships between long-term ocean warming, marine heat waves and primary production in the New Zealand region. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research.