Intro
The concept of the ‘right to repair’ has been on my mind recently, both as a user of tech products and as a designer of online courses. Electronics are notorious these days for their enigmatic design. The user is not trusted to make repairs or is restricted in the ways they can interact with device components. This is a choice made by manufacturers to limit access to approved vendors or repair shops. Instructional Designers have a similar choice when building courses. Do we follow a restrictive approach to modifications, or open up courses by anticipating, welcoming, and providing the resources for modifications?
Difficult by design
I recently experienced the restrictive side myself as I needed to fix an air purifier that had an unfortunate run-in with my youngest child and her colorful stickers. Apparently, the inside of the machine was not pretty enough, and the stickers were now stuck inside the machine, not quite clogging up the fan, but making a noticeable noise when the purifier was running. Realizing that I should probably remove them from the mechanism, and the partially obstructed fan, I grabbed my handy screwdriver, and rotated the cylindrical case to find where to begin.
And then I saw it – nothing. There were no screws on the outer shell. I turned it around a few more times, holding on to some hope that there was another way in – some switch to press or clasp to unhook. Nothing. The company designed the device to prevent a consumer from taking it apart. The only thing I had access to was the filter opening. No screws inside there either, and the manual had no sections on repairing the device.
I was put into a situation where I knew what I needed to do, and how to do it, but had no way of accomplishing it. If I tried to open it in a way it was not designed to be (whatever that was), I risked breaking the device even further, and voiding the warranty.
This is the situation many technology users find themselves in these days, which has led to a push for the right to repair one’s own devices.
Right to repair principles
Had the manufacturer made the air purifier with the consumer in mind, it may have been more closely aligned with right to repair principles, which are given by The Repair Association through their Policy Objectives. Some more relevant ones are currently paraphrased on the Right to repair – Wikipedia article:
- the device should be constructed and designed in a manner that allows repairs to be made easily;
- end users and independent repair providers should be able to access original spare parts and tools (software as well as physical tools) needed to repair the device at fair market conditions;
- repairs should by design be possible and not hindered by software programming;
- the repairability of a device should be clearly communicated by the manufacturer.
Applicability to Instructional Design
This whole endeavor got me thinking: What is the best choice for designers and developers who create courses and complex elements for our users? It seems that it falls into the same design philosophy choices that we see with other products like computer hardware or electronics today. For simplicity’s sake, let’s narrow it down to these two opposite choices designers have when making course components:
- Modifying course elements is made difficult because the designer is either not confident in the instructor’s abilities to properly work with the design, actively discouraging changes, thus resulting in no change until the user approaches the designer(s) again.
- Course elements are designed with user modifications in mind, and the user is left with sufficient instructions, access, and ability to make changes when necessary.
I prefer to use technology that closely follows the second choice, as this is more aligned with the ‘right to repair’, and results in more user-friendly practices. That is not to say that everyone would want to modify courses, but the option should be there.
Or, in other words:
It is the philosophical difference between engineering things to make them harder for the end user because you don’t trust them and documenting things to educate the end user so you know you can trust them.
Linus Sebastian, talking about the design choices of a pro-repair consumer laptop
If the previous main points of “right to repair” were to be re-written with online education in mind, how would these look? Perhaps something like this:
- The course and its objects should be constructed and designed in a manner that allows edits to be made easily.
- Instructors and SMEs should be able to access course components and tools needed to modify the course and its elements.
- Revisions and additions should be possible and not hindered by design choices.
- The Instructional Designer should clearly communicate the ability to modify the course, and how to do it.
How we could do it
What could we do as course designers to inform and empower faculty? Here are a few ideas:
General Documentation for Course Elements
By far one of the simplest ways to provide support to users is through basic documentation pages. If located on the course site itself, they can remain unpublished so learners do not see them. For those who would like more autonomy over their course structure and design, detailed documentation pages provide an excellent way to take the initiative and make the desired edits. Well-written documentation may also reduce the need for Instructional Designer support after the course is running. Plus, if you, as the designer, are worried about things breaking, you can always have a backup of all materials ready to revert pages.
Side by Side Code Blocks Tutorials
I use these all the time with fellow designers. On a Learning Management System (LMS), these function as a tutorial page where the page is split into two columns. Users can see the HTML/CSS code on the left and how it is displayed on the right. Then it’s a matter of copying the code from the code block and pasting it where they want it to go. This practice is very useful when it comes to the more advanced features of your LMS. This makes it easier to choose which element a user wants to incorporate or edit.

Learner Journey and Alignment
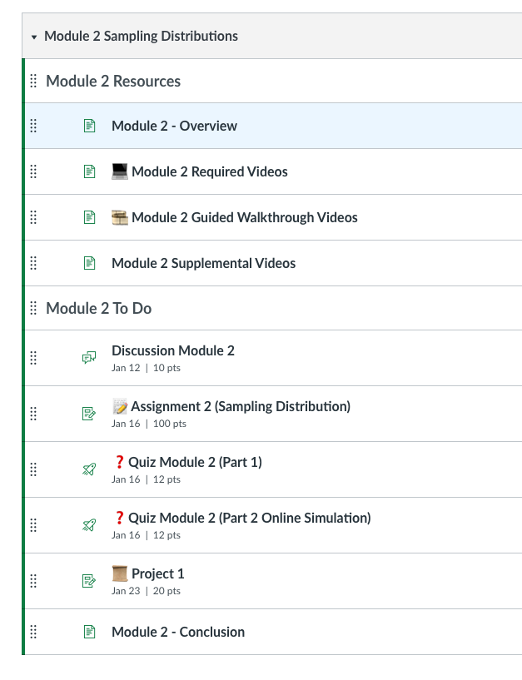
If an instructor wants to change the course a few terms after it has been running, how do we achieve a similar look and feel to the one created by the Instructional Designer long after the project has been developed? Mapping the expected learner journey, and how the content aligns with learning outcomes, can help with this. For example, imagine the learner is expected to interact with a week-long module by completing the following tasks in this order:
- Step A (Fulfills Learning Outcomes 1, 3. Informs Steps C and D)
- Step B (Fulfills Learning Outcome 2. Informs Steps C and D)
- Step C (Fulfills Learning Outcomes 3, 4)
- Step D (Fulfills Learning Outcome 1, 4)
Each step may include reading or watching learning materials, completing an assignment, participating in a discussion, and so on. How would this expected behavior change if, later on, an instructor added an additional assessment between C and D? What about removing Step B entirely (which in this example would remove alignment to Learning Outcome 2 from the module). Would a learner on this new version of the course still have the required information to complete the remaining parts of the module? Would they interact with the content in the same order as initially expected (and how the course was likely designed to be completed)?
These are things Instructional Designers plan and check during the initial development which can be shared to ensure that the same methods are followed in subsequent iterations of the course.
Conclusion
Some may prefer to leave everything in the hands of an experienced Instructional Design team, and use their expertise whenever a change is required. For others who have enough technical skills to edit content, the desire to learn more, or would like more autonomy and ownership over course content, an open course design provides the same user-friendly approach that at ‘right to repair’ would have for general electronics.
References
- Right to Repair, Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Right_to_repair
- Policy Objectives, The Repair Organization: https://www.repair.org/policy
- Linus Tech Tips: https://www.youtube.com/c/LinusTechTips