By: Julie Jacobs, Jana King, Dana Simionescu, Tianhong Shi
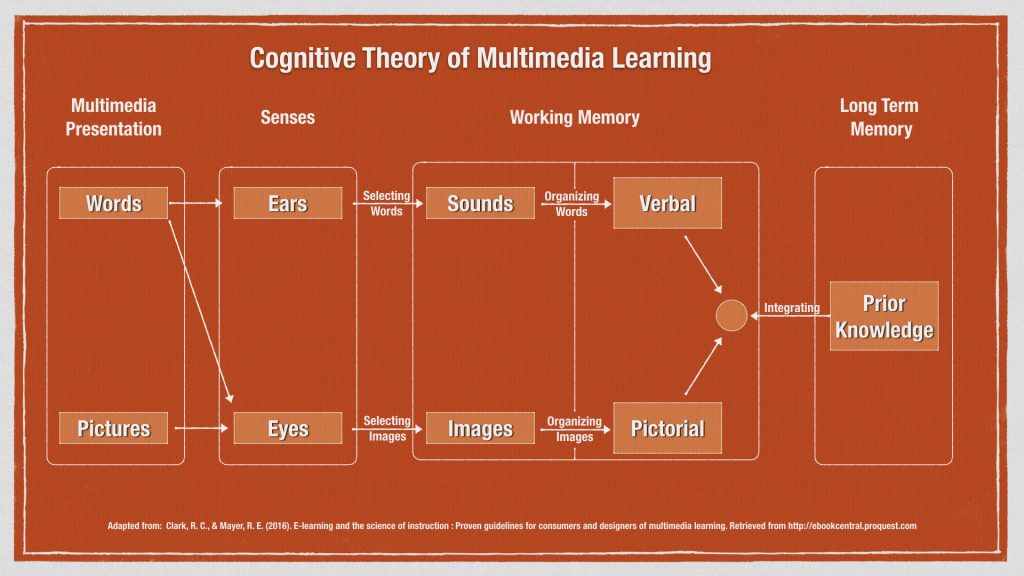
Overview
A recent scenario with our course development team challenged our existing practices with lecture media. Formerly, we had encouraged faculty to include only slides with narration in their lecture videos due to concerns about increasing learners’ cognitive load. Students voiced their hope for more instructor presence in courses, and some instructors started asking about including video of themselves inserted into their lectures. This prompted us to begin thinking about instructor presence in lecture videos more deeply: why were we discouraging faculty from including their faces in lecture videos? While our practices were informed by research-based media theory, we also recognized those theories might be outdated.
We began to explore the latest research with the following question in mind: does visual instructor presence in lectures increase extraneous cognitive load in learners? We use the phrase “visual instructor presence” to refer to lecture videos where an instructor’s moving image is seen giving the lecture, composited together with their slides. This technique is also commonly referred to as “picture-in-picture”, as seen in the image below.
Image 1: Adam Vester, instructor in College of Business, in his lecture design for BA 375 Applied Quantitative Methods.
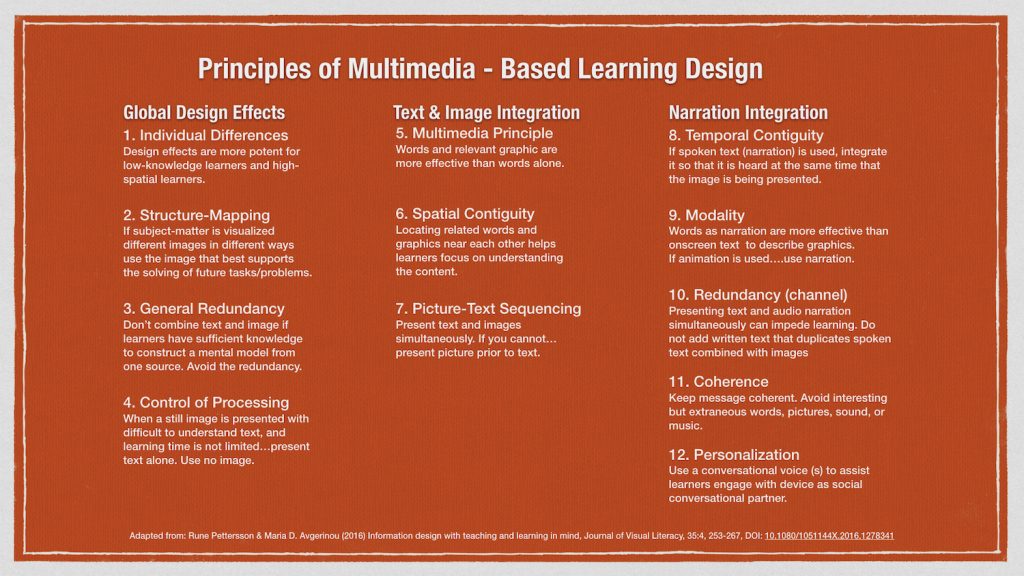
A task force was created to review recent research on visual instructor presence and cognitive load, specifically in lecture-type videos. Our literature review included a look at leading multimedia learning scholar Richard E. Mayer’s newest group of principles. We also reviewed more than 20 other scholarly articles, many of which were focused on learner perception, motivation & engagement, and emotion.
Findings
According to recent work in multimedia learning, research in this area should focus on three areas, namely learning outcomes (“what works/ what does not work?”), learning characteristics (“when does it work?”), and learning process (“how does it work?”) (Mayer, 2020). Below are our conclusions from the 23 research articles we reviewed regarding instructional videos, attempting to answer the above questions of “what works”, “when does it work”, and “how does it work”.
- This review of recent literature shows no evidence that visual instructor presence increases extraneous cognitive load.
- Students tend to prefer lectures with visual instructor presence – they report increased satisfaction and better perceived learning, which can boost motivation and engagement.
- While some studies find no difference in performance outcomes when visual instructor presence is utilized, others found increased performance outcomes with visual instructor presence. Proposed explanations: embodiment techniques such as gestures, eye contact, and body movement which fosters generative processing (the cognitive processes required for making sense of the material); social cues can help direct the learners’ attention; increased motivation (as per point 2 above) contributes to better learning.
- The effects may depend on the specific type of visual instructor presence (e.g., small picture-in-picture, green-screen, or lightboard) and the characteristics of the content (complex/difficult vs simpler/easier).
Recommendations
Based on these findings, our team has decided to remove the default discouragement of instructors wishing to use picture-in-picture in lectures. If an instructor is interested in having their visual presence in the lectures, we encourage them to discuss this option with their Instructional Designer and Lecture Media Coordinator to determine if this style is a good fit for them and their content.
Image 2: Bryony DuPont, associate professor of Mechanical Engineering, utilizing visual instructor presence in her lecture design for ME 382 Introduction to Design.
We recommend considering the following points:
- What is their presentation style? Do they tend to spend a lot of time talking over a slide or is there a lot of text or other action (e.g. software demo) happening in the video? If there’s a lot happening on the screen, perhaps it’s better to not put their video on top of it (the instructor video could be placed only at the beginning and/or end instead).
- What type of content? Is it simple or more complex? For more visually complex content, a lightboard or digital notation without picture-in-picture may work better, to take advantage of the dynamic drawing principle and the gaze guidance principle.
- Is it a foreign language course? If so, it’s likely helpful for the learners to see the instructor’s mouth and body language.
- Is the instructor comfortable with being on video? If they’re not comfortable with it, it may not add value. This being said, our multimedia professionals can help make instructors more comfortable in front of the camera and coach them on a high-embodied style of lecturing.
Since implementing these guidelines and working with an increased number of lectures with visual instructor presence, we also noticed that it works best when the instructor does not look and sound like they’re reading. Therefore, for people who like working with a script, we recommend practicing in advance so they can sound more natural and are able to enhance their presentation with embodiment techniques.
We would love to hear about your opinions or experiences with this type of video. Share them in the comments!
For a detailed summary of our findings and full citation list, please see the full Literature Review.







 For DIY video production, there are many ways to go about this!
For DIY video production, there are many ways to go about this!