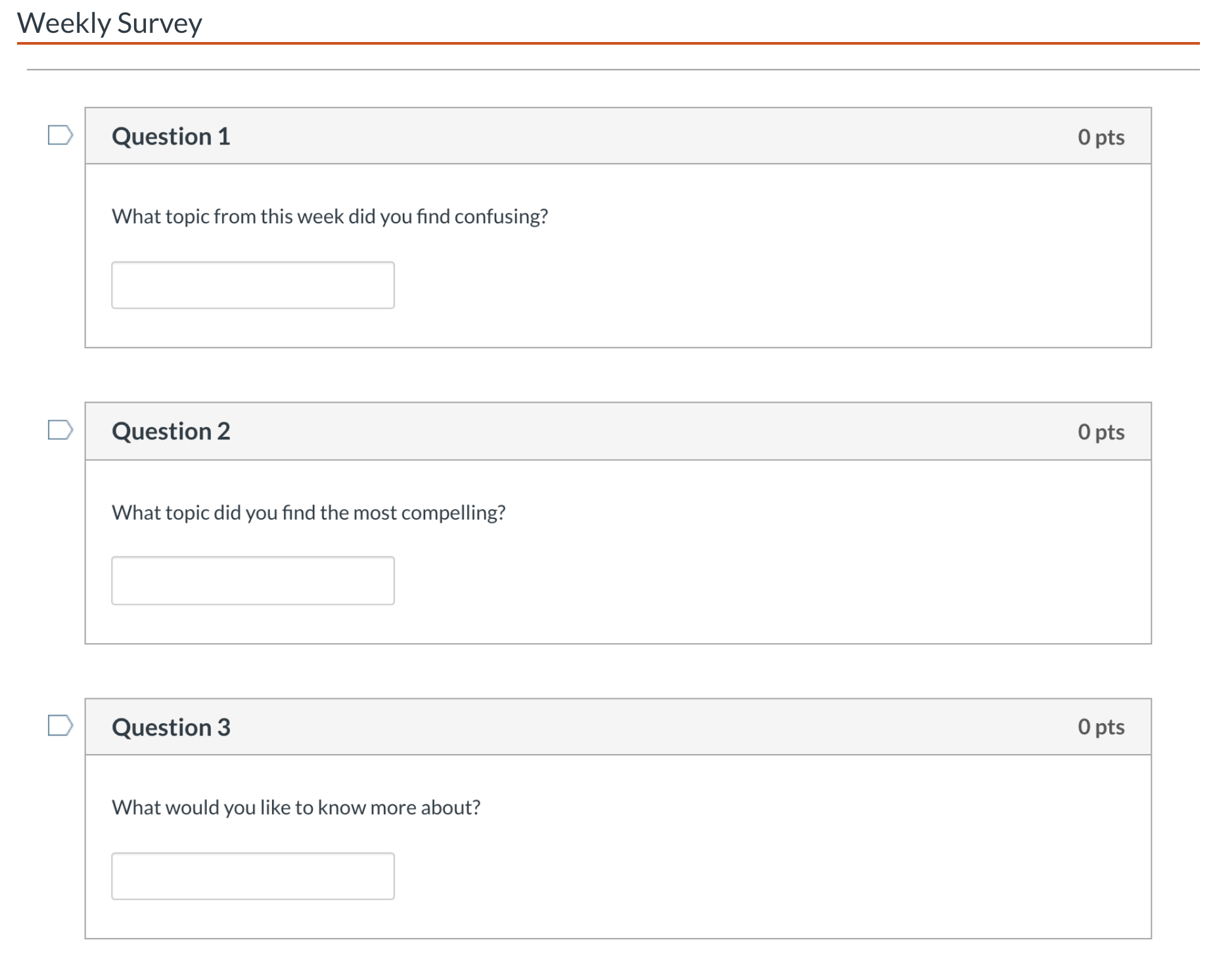
This is the paradox of failure in games. It can be stated like this:
- We generally avoid failure.
- We experience failure when playing games.
- We seek out games, although we will experience something that we normally avoid. (Juul, p. 2)
As a continuation from my last blog post considering grades and Self-Determination Theory, I wanted to take a brief side-quest into considering what it means to experience failure. Jesper Juul’s The Art of Failure: An Essay on the Pain of Playing Video Games will provide the main outline and material for this post, while I add what lessons we might learn about feedback and course design in online settings.
Dealing with Failure
Juul outlines how games communicate through feedback using the theory of Learned Helplessness. Specifically, he focuses on Weiner’s attribution theory, which has three dimensions:
- Internal vs. External Failure
- Internal: The failure is the fault of the player. “I don’t have the skills to defeat this enemy right now.”
- External: The failure is the fault of the game. “The camera moved in a way that I couldn’t see or control and resulted in a game over.”
- Stable vs. Unstable Failure
- Stable: The failure will be consistent. No recognition of experience gained or improvement. “No matter what I do, I can’t get past this challenge.”
- Unstable: The failure is temporary. There is a possibility for future success. “I can improve and try again.”
- Global vs. Specific Failure
- Global: There is a general inability preventing success. “I am not good at playing video games.”
- Specific: Poor performance does not reflect on our general abilities or intelligence. “I’m not good at flight simulators, but that doesn’t mean I’m bad at all video games.”
In general, a combination of Internal+Stable+Global failure feedback would contribute most strongly toward a player adopting a learned helplessness mindset. There is a potential parallel here with course design: when a student does not do well on an assessment, what kind of feedback are they receiving? In particular, are they receiving signals that there is no opportunity for improvement (stable failure) and that it shows a general inability at the given task (global failure)? Designing assessments so that setbacks are unstable (offer multiple attempts and a way for students to observe their own improvement over time) and communicating specific skills to improve (make sure feedback pinpoints how a student could improve) would help students bounce back from a “game over” scenario. But what about internal vs. external failure? For Juul, “this marks another return of the paradox of failure: it is only through feeling responsible for failure (which we dislike) that we can feel responsible for escaping failure (which we like)” (p. 54). This importance of internal failure aligns with what we know about metacognition (Berthoff, “Dialectical notebooks and the audit of meaning”) and the numerous benefits of reflection in learning.
Succeeding from Failure
Now that we have an idea on how we deal with failure, let’s consider how we can turn that failure into success! “Games then promise players the possibility of success through three different kinds of fairness or three different paths: skill, chance, and labor” (Juul, p. 74):
- Skill: Learning through failure, emphasis on improvement with each attempt. (This is also very motivating by being competence-supportive!)
- Chance: We try again to see if we get lucky.
- Labor: Incremental progress on small tasks accumulates more abilities and items that persist through time and multiple play sessions. Emphasis here is on incremental growth over time through repetition. (Animal Crossing is a great example.) (This path is also supported by Dweck’s growth mindset.)
Many games reward players for all three of these paths to success. In an online course, allowing flexibility in assignment strategies can help students explore different routes to success. For example, a final project could allow for numerous format types, like a paper, podcast, video tutorial, interactive poster, etc. that students choose strategically based on their own skills and interests. Recognizing improvement will help students with their skills and helping students establish a routine of smaller, simpler tasks that build over an entire course can help them succeed through labor. Chance is an interesting thing to think about in terms of courses, but I like to think of this as it relates to content. Maybe a student “gets lucky” by having a discussion topic align with their final project topic, for example. For the student in that example, that discussion would come easier to them by chance. Diversifying content and assignment types can help different individuals and groups of students feel like they have “lucky” moments in a course.
Reflecting on Failure
Finally, how do games give us the opportunity to reflect on our successes and failures during gameplay? Juul outlines three types of goals that “make failure personal in a different way and integrates a game into our life in its own way” (pp. 86–87):
- Completable Goal: Often the result of a linear path and has a definite end.
- These can be game- or player-created. (i.e., Game-Driven: Defeat the ghost haunting the castle. Player-Driven: I want to defeat the ghost without using magic.)
- Transient Goal: Specific, one-time game sessions with no defined end, but played in rounds. (e.g., winning or losing a single round of Mario Kart.)
- Improvement Goal: Completing a personal best score, where a new high score sets a new goal.
For Juul, each of these goal-types have different “existential implications: while working toward a completable goal, we are permanently inscribed with a deficiency, and reaching the goal removes that deficiency, perhaps also removing the desire to play again. On the other hand, we can never make up for failure against a transient goal (since a lost match will always be lost), whereas an improvement goal is a continued process of personal progress” (pp. 86–87). When thinking about your courses, what kinds of goals do you design for? Many courses have single-attempt assignments (transient goal), but what if those were designed to be improvement goals, where students worked toward improving on their previous work in a more iterative way that replaced old scores with new and improved scores (improvement goal)? Are there opportunities for students to create their own challenging completable goals?
I hope this post shines a light on some different ways of thinking about assessment design, feedback types, and making opportunities for students to “fail safely” based on how these designs are achieved in gaming. To sum everything up, “skill, labor, and chance make us feel deficient in different ways when we fail. Transient, improvement, and completable goals distribute our flaws, our failures, and successes in different ways across our lifetimes” (Juul, p. 90).