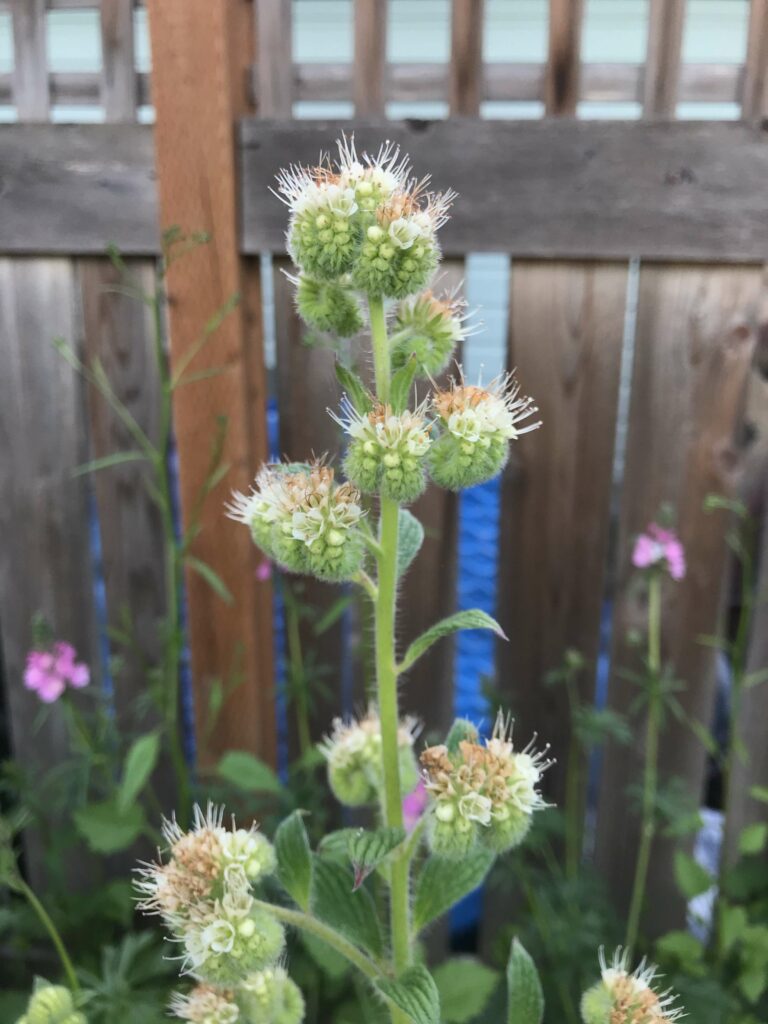
The Garden Ecology Lab’s Pollinator Plant PR Campaign Presents….. Common Madia (AKA Tarweed)!
The Garden Ecology Lab is releasing a series of plant profiles of the top 10 Oregon native plants for pollinators, based on Aaron Anderson’s 2017-2019 field trials of 23 Oregon native plants. We will feature one plant per week for 10 weeks, this is week 6! Profiles will include photos, planting information, and will highlight common pollinators of each plant.

some rights reserved
Plant Facts
- Scientific Name: Madia elegans
- Life Cycle: Annual
- Growth Habit: Erect, slender
- Bloom Duration: July – September
- Hardiness Zone: 1-11
- Light requirements: Prefers full sun, will tolerate partial shade.
- Special Traits: Drought tolerant, deer resistant, seeds valued by birds, adaptable to many soil types and textures.
- When to plant: Seeds can be sown directly in the fall, or sown in containers or cold frames in the winter. Stratify seeds if growing indoors.
Pollinator Facts
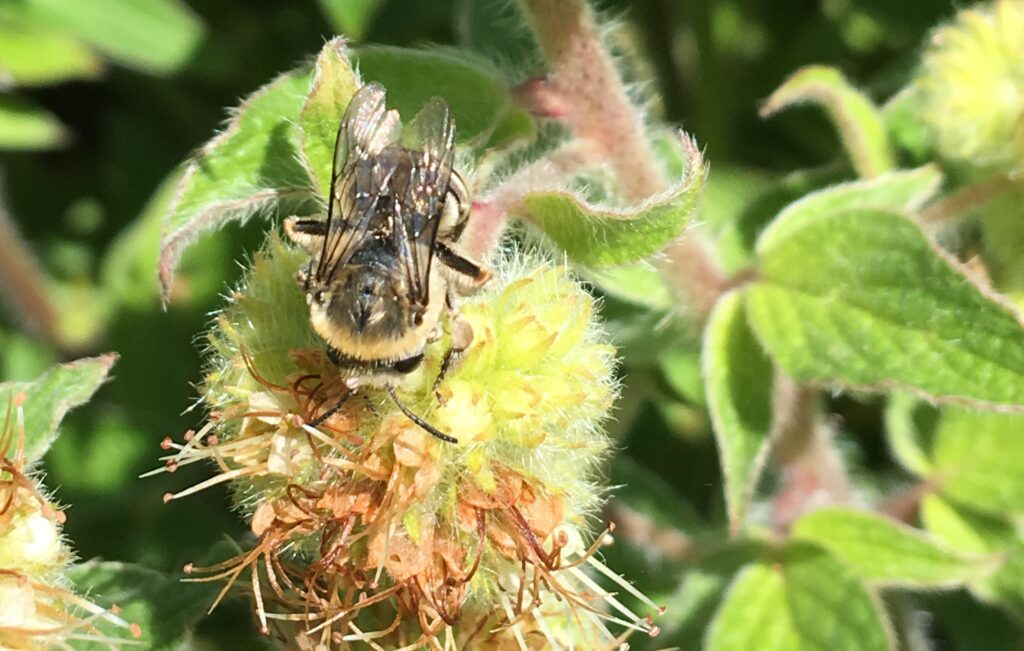
- Common madia provides both nectar and pollen to its insect visitors and blooms during a period where foraging resources are often scarce (late summer – early fall).
- Madia was found to be associated with two bee species in Aaron’s research: the Bi-colored Sweat Bee (Agapostemon virescens) and Titus’s Sweat Bee (Lasioglossum titusi)
- Madia is also the larval host for three moth species: the Spotted Straw Sun Moth (Heliothis phloxiphada), the Small Heliothodes Moth (Heliothodes diminutivus), and an Epiblema moth (Epiblema deverrae)1.

some rights reserved
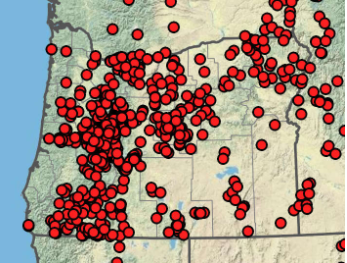
Common Madia‘s Native Range in Oregon

Madia elegans is native to most of Western Oregon. Although it's native range does not extend east of the Cascades, it is a hardy annual that may do well in Central- and Eastern- Oregon gardens. Map acquired from Oregon Flora with imagery sourced from Google.
Common Madia as a pollinator plant
Common Madia is an ideal plant for pollinator gardens due to its long bloom duration and attractiveness to bees, caterpillars, and butterflies. Madia was found to attract both a high abundance and a high diversity of bee visitors, which further speaks to its use as a great pollinator plant! Due to it’s late-summer bloom period, Madia can act as a great source of forage for it’s various visitors when there may not be many other plants flowering in the landscape. Madia flowers, which close at dusk and reopen in the morning, may also come with a fun surprise if you catch them before the sun has finished its ascent: if you’re lucky, you may be able to find male long-horned-bees sleeping in groups within the flowers2.


Infographics developed by LeAnn Locher, Aaron Anderson, and Gail Langellotto.
Abundance Calculations. Bee abundance was calculated using estimated marginal means of bee visitation to each of our study plants from 5-minute observations conducted from Aaron’s 2017-2019 field seasons. Estimated marginal means (EM Means) were assigned to categorical values and averaged across years to yield the following categories: 0% = Very Low =EM mean below 0.49; 25% = Low = EM mean of 0.50 to 0.99; 50% = Moderate = EM mean of 1 to 1.49; 75% = High = EM mean of 1.50 to 1.99; and 100% = Very high = EM mean above 2.0.
Diversity Calculations. Bee diversity was based on the total sum of species collected on each of our study plants from 2017 to 2019. A Chao 2 Estimator was used to estimate total expected species richness for each plant; Chao 2 estimates were then used to create categorical values, as follows: 0% = Very Low = 9.99 or lower; 25% = Low = 10 to 14.99; 50% = Moderate = 15 to 19.99; 75% = High = 20 to 24.99; 100% = Very high = 25 or higher.
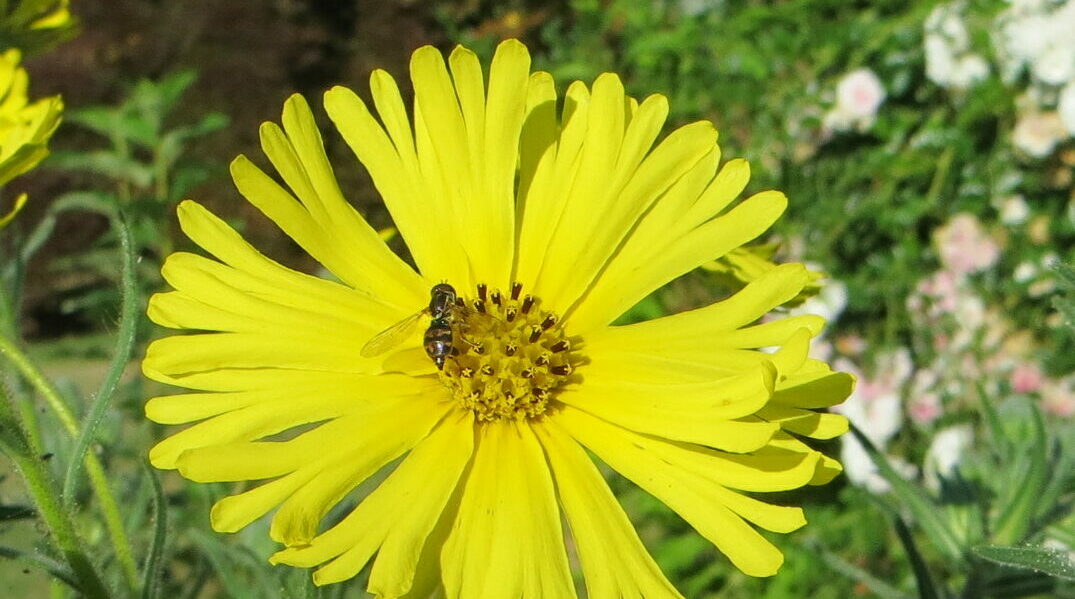

Did you know?
The other common name for Madia, “Tarweed”, comes from its foliage. It’s covered in stiff trichomes (hairs) and stalked glands which emit a tar-like scent. Common Madia is not the only species with this nickname, it applies to plants in the entire genus! For example, Madia glomerata, “Mountain Tarplant”, is a species of Madia native to the Northeast United States.
Common Madia‘s fruits are flattened achenes, which are valued by small mammals and birds as a food source. The achenes were also used by Indigenous groups, including the Pomo, Miwok, and Hupa and as a staple food source3. The fruits were often roasted with hot coals and then ground into flour.
Photos from the field
Tune in next week for the next edition of our Pollinator Plant PR Campaign.