
This blog post is an Instructor Spotlight authored by Xiaohui Chang. Xiaohui is a Toomey Faculty Fellow and Associate Professor of Business Analytics in the College of Business. This post is a follow up to Improving Student Engagement and Connection in Online Learning: Part I, Proactive Support.
Introduction
Since the first post in the series appeared a few months ago, we have received plenty of feedback from other instructors who are actively engaged in online education. Some of the stories shared by them reiterate the points we discussed, and others included tips and techniques that have worked particularly well for them. Almost all of them agreed that teaching well online remains a challenging task.
“I love the notes on proactive student support … especially the notes on checking in with those who are behind. Sometimes all they need is a little empathy!”
Vic Matta, Associate Professor, College of Business, Ohio University
“I regularly incorporate each of these in my relationships with my students, to include weekly zoom “what’s up” meetings with my students. I check in on them if they’re behind on assignments…Yes, it takes effort; but my mission is to help these students find the greatness within themselves to succeed.”
To quickly recap what we have discussed in Part 1, we touched on how to employ empathy statements in communications with students, restructure and promote the office hours, provide personal feedback for students, and periodically check in with students who are behind. You may also refer to the first article here: Improving Student Engagement and Connection in Online Learning: Part I, Proactive Support.
Continuing from the first post, Part II will revolve around six specific practices that I have found particularly helpful for online teaching and learning.
Practice 1: Adopt a variety of communication methods
I provide assignment instructions and guidance using a variety of communication methods including texts, diagrams, images, and short video clips. I have learned that instructions with screenshots and videos tend to be better in explaining complicated procedures than text alone.
Video Tutorial Example: Creating a random sample using XLSTAT
Practice 2: Create a Q&A Discussion Board
I have a separate discussion on Canvas for students to address issues with the class in general (content questions, technical issues, deadlines). Instead of emailing the instructor regarding issues other students may also have questions about, students are encouraged to use this forum so that all can benefit from the questions and answers. I usually wait for a few hours for students to answer each other’s questions first before I provide mine.
When students email me questions that are a good fit for the Q&A Discussion Board, I’d respond through email first and then recommend the students submit the questions to the discussion board so that other students can learn from the questions and answers. This discussion board also creates an inviting and engaging learning environment for the students who don’t get to meet their classmates in a face-to-face setting.
Practice 3: Estimate the amount of time taken for each assignment
I was skeptical of this at first as the time taken would vary drastically for each individual. However, student feedback indicates that estimated times helped them plan for the week and set aside an appropriate amount of time. We don’t need to worry too much about making the estimates accurate for everyone as students will automatically adjust given their own work styles. A workload calculator that I have found helpful is developed by the Center for Advancement of Teaching at Wake Forest University, called the Workload Estimator 2.0.
For more information about estimation rates, see the explanation here – Workload Estimator: How We Calculated.
Practice 4: Ensure timely replies
This practice is obvious, but difficult to do when one is teaching multiple sessions with hundreds of students. For online classes, timely replies make students feel as though they are taking an in-person class with all of the built-in support and resources. I understand that we all have different teaching priorities and schedules, however, it all comes down to figuring out how to most efficiently organize our days so that we can be available to students.
Setting aside a couple of times a day for handling emails has worked quite well for me, e.g., the first thing in the morning, after noon, and before the end of the day. I try my best to respond to students’ emails within 24 hours and check my mailbox at least once every day on the weekends.
The timely replies in discussions were super helpful. It really felt as though I took this in person with all of the built-in help and support.
Student quote
Practice 5: Synchronize assignments with Canvas calendar
I have also synced all assignments and my office hours (renamed as Ask Me Anything Hours) on Canvas so that there are office hours available around when assignments are due. This proves to be incredibly convenient and useful for both students and instructors.
Practice 6: Reorganize course content
Here are several Canvas LMS tips that have helped in organizing the course content and saved my time. I try to organize everything in modules. Under each module, all items are split into two main components: resources and to-do lists, so students know exactly what assignments they would need to complete for each module. I also adopt a fixed set of systems for titling Canvas items. Items within modules are indented to help with organization.
Weekly agenda and announcements are also hyperlinked to guide students with the course navigation. I could not emphasize enough how much I value the internal messaging in the Canvas grade book that was briefly discussed in my previous post. This feature allows instructors to message students who haven’t submitted yet or who scored less than a certain point. Definitely a slick way to send quick emails to a target group.
Recently, I have been experimenting with a range of visual cues (e.g., emojis) to categorize course content. An example is provided below.
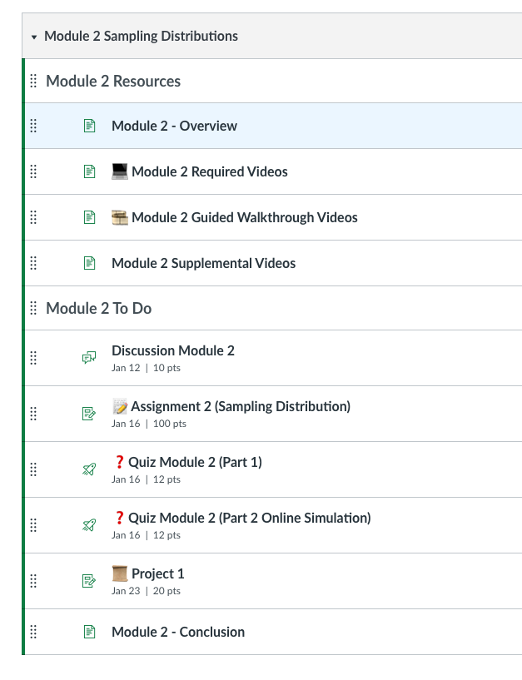
There was also a recent post on using emojis for visual way finding and fostering a friendly tone in online classes here: My Experience with Emojis in Online Courses: Affordances and Considerations.
Conclusion
It’s always best to keep an open mind when trying out new teaching practices and adapt them to your individual style and subject matter.
If you have any online teaching practices that you’re fond of, please feel free to contact me at Xiaohui.Chang@oregonstate.edu as I will be very excited to hear them and test them out.

