David P. Turner / August 4, 2022
Given the vast amount of order in the universe, can humans reasonably hope to add a new increment of order in the form of a sustainable, high-technology, global civilization?
On the plus side, the universe is said to be order-friendly. Complexity is a rough measure of order, and we can observe that from its Big Bang origin to the present, the universe displays a gradual build-up of complexity. Systems theorist Stuart Kaufmann says that we are “at home in the universe” and he emphasized the widespread occurrence of self-organization (Figure 1). From atoms to molecules, to living cells, to multicellular organisms, to societies, to nation states – why not onward to a sustainable planetary civilization?
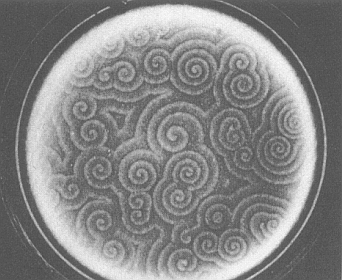
Figure 1. The Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction. This mixture of chemicals generates geometric forms (order) that oscillate until chemical equilibrium is reached.
Whether the universe is order-friendly or not is of course not strictly a scientific question, but scientists do aspire to explain the origins and elaboration of order. Broadly speaking, they refer to the process of cosmic evolution with its components of physical evolution, biological evolution, and cultural evolution. Cosmic evolution is a unifying scientific narrative now studied by the discipline of Big History; it covers the temporal sequence from Big Bang to the present, emphasizing the role of energy transformations in the buildup of complexity.
Physical evolution of the universe consists of the emergence of a series of physical/chemical processes powered by gravity. Formation of the higher atomic weight elements by way of fusion reactions in successive generations of stars is a particularly important aspect of physical evolution because it sets the stage for the inorganic and organic chemistry necessary for a new form of order – life.
Biological evolution on Earth began with single-celled organisms, and by way of genetic variation and natural selection, led to the vast array of microbes and multi-cellular organisms now extant. Each creature is understood as a “dissipative structure”, which must consume energy of some kind to maintain itself and reproduce. Biological evolution produced increments of order – such as multicellularity – because each step allows for new capabilities and specializations that help the associated organisms prevail in competition for resources.
Scientists are just beginning to understand how biological evolution favors cooperation among different types of organisms at higher levels of organization. Ecosystems, which are characterized by energy flows and nutrient cycling, depend on feedback relationships among different types of organism (e.g. producers, consumers, decomposers). The biosphere (i.e. the sum of all organisms) is itself a dissipative structure fueled by solar energy. Biosphere metabolism participates in the regulation of Earth’s climate (e.g. by its influence of the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere), thus making the planet as a whole an elaborate system, now studied by the discipline of Earth System Science.
Cultural evolution introduces the possibility of order in the form of human societies and their associated artifacts. It depends on the capacity for language and social learning, and helps account for the tremendous success of Homo sapiens on this planet. As with variation and selection of genes in biological evolution, there must be variation and selection of memes in the course of cultural evolution. In the process of cultural evolution, we share information, participate in the creation of new information, and establish the reservoirs of information maintained by our societies.
The inventiveness of the human species has recently produced a new component of the Earth system – the technosphere. This summation of all human artifacts and associated processes rises to the level of a sphere in the Earth system because it has become the equivalent of a geologic force, e.g. powerful enough to drive global climate change.
Unfortunately, the technosphere is rather unconstrained, and in a sense its growth is consuming the biosphere upon which it depends (e.g. tropical rain forest destruction). Technosphere order (or capital) is increasing at the expense of biosphere order. The solution requires better integration within the technosphere, and between the technosphere and the other components of the Earth system – essentially a more ordered Earth system.
How might the technosphere mature into something more sustainable? One model for the addition of order to a system is termed a metasystem transition. I have discussed this concept elsewhere, but briefly, it refers to the aggregation of what were autonomous systems into a greater whole, e.g. the evolution of single-celled organisms into multicellular organisms, or the historical joining of multiple nations to form the European Union.
In the case of a global civilization, the needed metasystem transition would constitute cooperation among nation states and civil society organizations to reform or build new institutions of global governance, specifically in the areas of environment, trade, and geopolitics. Historically, the drivers of ever larger human associations have included 1) the advantages of large alliances in war, and 2) a sense of community associated with sharing a religious belief system. But perhaps in the future we might look towards planetary citizenship. Clear benefits to global cooperation would accrue in the form of a capacity to manage global scale threats like climate change.
Conclusion
Living in an order-friendly universe allows us to imagine the possibility of global sustainability. However, the next increment of order-building on this planet will require humans and humanity to take on a new level of responsibility.
Biological evolution gave us the capacity for consciousness and now we must use guided cultural evolution to devise and implement a pathway to global sustainability. Besides self-preservation, the motivation to do so has a moral dimension in terms of 1) minimizing the suffering of relatively poor people who have had little to do with causing global environmental change but are disproportionately vulnerable to it, 2) insuring future generations do not suffer catastrophically because of a deteriorating global environment caused by previous generations, and 3) an aesthetic appreciation or love (biophilia) for the beauty of nature and natural processes.
Our brains, with their capacity for abstract thought, are the product of biological evolution. They were “designed” to help a bipedal species of hunter-gatherers survive in a demanding biophysical and social environment. Hence, they don’t necessarily equip us to understand how and why the universe is order-friendly. But we can see the pattern of increasing complexity in the history of the universe, and aspire to move it forward one more step – to the level of a planetary civilization.
