Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) describes an online resource requested from another outside domain. This is most often done by web pages making HTTP/AJAX requests to other web servers to retrieve external resources such as images, stylesheets, and scripts.
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
While the CORS mechanism is necessary for the modern internet, it can also pose a security risk. A malicious attacker induces the victims to unintentionally share the user’s private information cookies or submit forms to perform privileged actions. These types of attacks are known as Cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
Same-Origin Policy (SOP)
As a result, most modern web browsers impose a Same-Origin Policy (SOP) to prevent malicious websites (or insecure websites injected with malicious code) to make requests or accessing data from another origin. The same-origin policy should also be implemented in the backend as well in case the user relaxed the SOP.
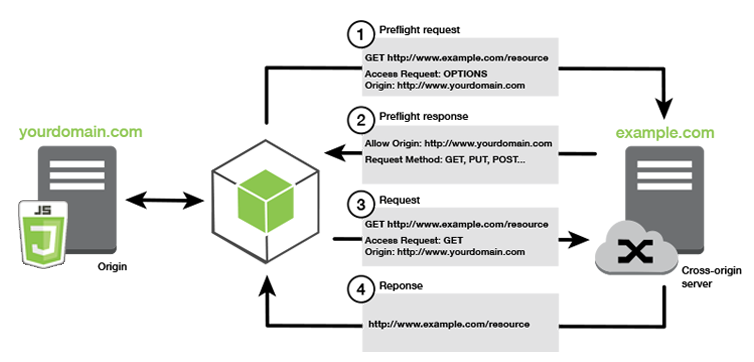
Preflights
Whenever a website wants to request external resources from another origin, web browsers will make a preflight request to the server checking if the server will permit the Cross-Origin Request. The preflight request will specify the origin of the cross-origin access request and HTTP method/headers that will be used. If the server approves of the Cross-Origin Request, then it will respond with the allowed origins, headers, credentials, methods, as well as how long the preflight request needs to be made again.
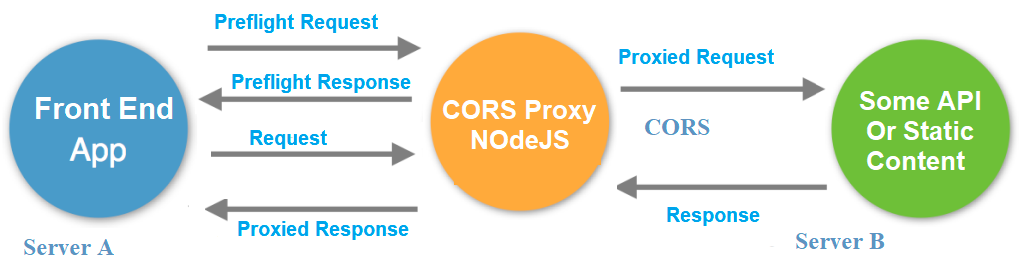
Bypass SOP using Proxy
I decided to look into this topic because I run into an issue with Same-Origin Policy. In the web application of Chicken Tinder, an HTTP call is made to the REST API in the backend every time the user creates/joins a flock and votes for restaurants. Since the URL of my backend API is hosted at a different origin from my front-end application, the browser would block the API call unless I decided to relax the SOP. This is obviously inconvenient and insecure for the users so I am in the process of resolving this issue. One way to circumvent the SOP restriction in a React App is to configure a proxy in package.json file, which will change all initially cross-origin requests to the backend (react app) server. One can also create a proxy server to make API calls on behalf of the client application.
Read more about CORS:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS#the_http_request_headers
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-origin_resource_sharing
https://portswigger.net/web-security/csrf
https://www.stackhawk.com/blog/react-cors-guide-what-it-is-and-how-to-enable-it/
