Prompt: Describe how microbial communities in the body could influence the brain and mental health states. Then describe how the brain and mental health states could influence microbial communities in the body. In what ways might these promote health and/or disease?
The microorganisms in your gut can break down pieces of the food we eat and produce things like fatty acids. Some of the fatty acids are thought to be beneficial to the brain. For example, butyrate is produced by microorganisms and is thought to help cell proliferation in the brain. A father did a case study on his child with autism and found that his GI symptoms and overall behavior improved when given antibiotics. The thought behind this is that the antibiotics would kill potentially harmful microorganisms and help relieve symptoms both in the GI and in the brain (behaviors). There are a few mechanisms of how microbial communities can influence the gut, here is a diagram of them.
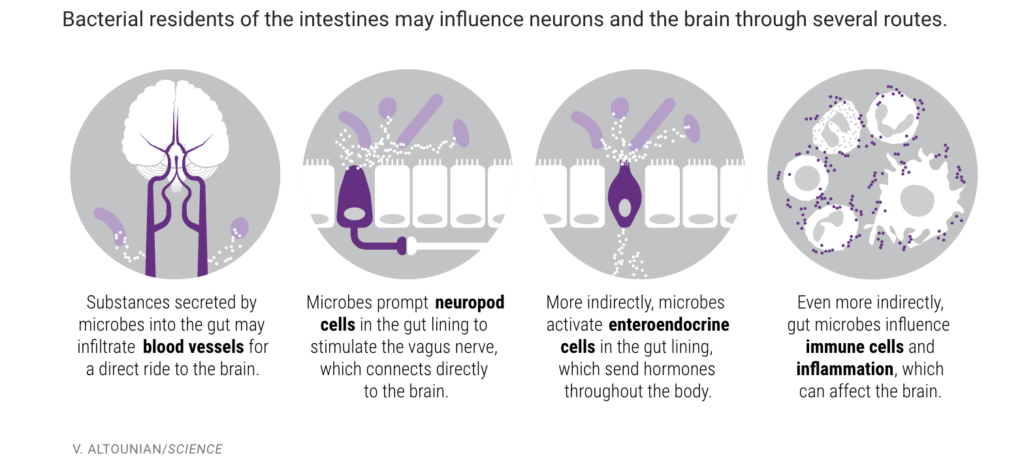
Researchers have found that there are higher rates of depression among those on antibiotics compared to anti-fungal or antiviral medications. This could be due to antibiotics creating dysbiosis in the gut microbiota. There is research that shows people with Alzheimer’s have a less diverse gut microbiome.
Overall, there is a connection between the gut and brain called the gut-brain axis. Stress can cause disruption of the gut microbiota. Stress signals from the brain travel through the vegus nerve to the gut cells which can impact the microorganisms home environment. The gene that is needed to develop Parkinson’s can possibly be triggered by a bacteria that is usually found on the skin migrating into the gut microbiota. It is also believed that strong emotions can affect secretion of gastric acid, bile, and mucus. This changes the environment that the microorganisms are living in.
All this research shows the importance of further progress of the gut-brain connection within the realm of microbiota. I think this shows the importance of paying attention to all the factors that we can individually control to make sure our gut microbiota is healthy.
Sources: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/gut-brain-connection https://www.science.org/content/article/meet-psychobiome-gut-bacteria-may-alter-how-you-think-feel-and-act http://depts.washington.edu/mbwc/news/article/the-gut-microbiome-and-brain-health https://fems-microbiology.org/gut-microbiome-and-mental-health/#:~:text=Additionally%2C%20stress%20and%20emotions%20affect,composition%20of%20the%20gut%20microbiome.
